Explain the Differences Between Type I and Type Ii Topoisomerases
Type II DNA topoisomerases are divided into two families IIA and IIB. In order to investigate the differences in the mechanism of these two prototypical type IA topoisomerases we studied DNA decatenation at the single-molecule level using braids of intact dsDNA and nicked dsDNA with bulges.

A The Mechanism Of Type I Dna Topoisomerase The Enzymes Nick A Download Scientific Diagram
Describe the general differences between the mechanisms of Type I and Type II topoisomerases.

. They use the hydrolysis of ATP unlike Type I topoisomerase. Types IIA and IIB enzymes share homologous B subunits encompassing the ATP-binding site but have non-homologous A subunits catalyzing DNA cleavage. Type-II topoisomerases pass one double-helix segment through another to allow changes in knotting of one mol-ecule or interlinking of double helices.
Yan J Magnasco MO Marko JF 2001 Kinetic proofreading can explain the supression of supercoiling of circular DNA molecules by type-II topoisomerases Physical Review E - Statistical Nonlinear and Soft Matter Physics vol. Type IIA topoisomerases are ubiquitous in Bacteria and Eukarya whereas members of the IIB family are mostly present in Archaea and. Both types have been proposed to use an enzyme-bridging mechanism in which a break is formed in a DNA strand and a gap is opened between the broken pieces to allow passage of a second DNA strand or duplex segment.
Negatively supercoiled DNA. In this paper series of synthesized quinoline quaternary ammonium salts with odd and even carbon number alkyl gr. The structural modification of quinolone derivatives has been a hot spot in recent years especially the modification of the N-1 position which is the part that this article focuses on.
Goto and Wang 1985. This result is often misinterpreted to indicate that the Δ Lk for each round of catalysis must be 1 for type I enzymes and 2 for type II enzymes. Type I topoisomerases Topo I introduce transient DNA single-stranded breaks in order to change the topological linking number of a double-stranded DNA molecule by steps of one whereas type II topoisomerases Topo II introduce transient double-stranded breaks and change the linking number by steps of two.
Type IA and type II DNA topoisomerases are distinguished by their ability to cleave one or two strands respectively of a DNA duplex. Explain in detail how a Type IA topoisomerase can relax a negatively supercoiled DNA molecule. Which induces an unusual type of DNA damage by trapping cellular topoisomerase I on.
In this process these enzymes change the linking number of circular DNA by 2. To examine the differences in the mechanism of these two related type IA topoisomerases single-molecule relaxation studies were conducted on several DNA substrates. The enzymes that pass DNA through DNA so as to remove entanglements adenosine-triphosphate-hydrolyzing type-II topoisomerases are able to suppress the probability of self-entanglements knots and mutual entanglements links between approximately.
Topoisomerases are ubiquitous enzymes found in all living organisms. In this paper series of synthesized quinoline quaternary ammonium salts with odd and even carbon number alkyl groups in N-1 position were used to explain the influence of the alkyl side chain. Topoisomerases transiently make either single-strand type I topoisomerases or double-strand type II breaks in DNA to prevent the build-up of topological stress and tangles as the genome is.
Important Differences between Topoisomerase-I and -II Targeting Agents. Topoisomerase II is a critical enzyme involved in unknotting and detangling DNA during replication transcription and cell division. A cccDNA molecule has an Lkº value of 52.
Whereas topoisomerase III is a more efficient decatenase than topoisomerase I the opposite is true for DNA relaxation. Will a topoisomer of this molecule with an. The structural modification of quinolone derivatives has been a hot spot in recent years especially the modification of the N-1 position which is the part that this article focuses on.
Type II topoisomerases are topoisomerases that cut both strands of the DNA helix simultaneously in order to manage DNA tangles and supercoils. Type I topoisomerase Type II topoisomerase Type III topoisomerase type IV topoisomerase Question Which type of enzyme makes a transient break in both DNA duplex strands and then transports another segment of a DNA molecule or separate molecule entirely through the break and reseals the severed strands. Difference between type I and type II topoisomerases is how they cut.
Most type-I topoisomerases are simple catalysts and act in. Type 2 topoisomerases break and rejoin both strands changing the linking number in increments of 2. Humans have two isoforms of topoisomerase II α Top2A and β Top2B originating from genes on separate chromosomes and displaying distinct functional roles.
Polymerase chain reaction PCR is a laboratory technique that allows scientists to perform DNA replication in a small tube using artificial. Uemura and Yanagida 1984 while TOP1 the structural gene for topoisomerase I is dispensable for viability in both organisms Thrash et al 1985. In addition these enzymes are the target of several.
Type-I topoisomerases transiently cut one of the double-helix back-bones to allow changes in internal duplex linking number. A type I topoisomerase breaks only one strand of the DNA whereas a type II topoisomerase breaks both strands of the DNA. Type I cuts one strand of the duplex to relieve supercoiling Type II cuts both strands of the duplex and induces ATP-dependent negative supercoiling requires ATP Both topoisomerases.
Because of this mechanistic difference the linking number of DNA L will change in increments of 1 or 2 for type I and type II topoisomerases respectively. Topoisomerases have been categorized into two types. Type 1 topoisomerases break and rejoin only one strand changing the linking number in increments of 1.
3 I 031909 pp. The DNA of virtually every cell is underwound ie negatively supercoiled relative to B-form DNA. Uemura and Yanagida 1984.
Up to 256 cash back Using what you know about hydrogen bonds explain why helicase is necessary to break hydrogen bonds in DNA but not necessary to break hydrogen bonds between the codon and anticodon. TOP2 the structural gene for topoisomerase II is an essential gene in both yeasts Goto and Wang 1984. Type I and II topoisomerases yield products that differ in DNA linking number Lk by 1 and 2 respectively 35.
What Is The Difference Between Topoisomerase I And Ii Pediaa Com

Topoisomerase Classifications And Characteristics Download Table
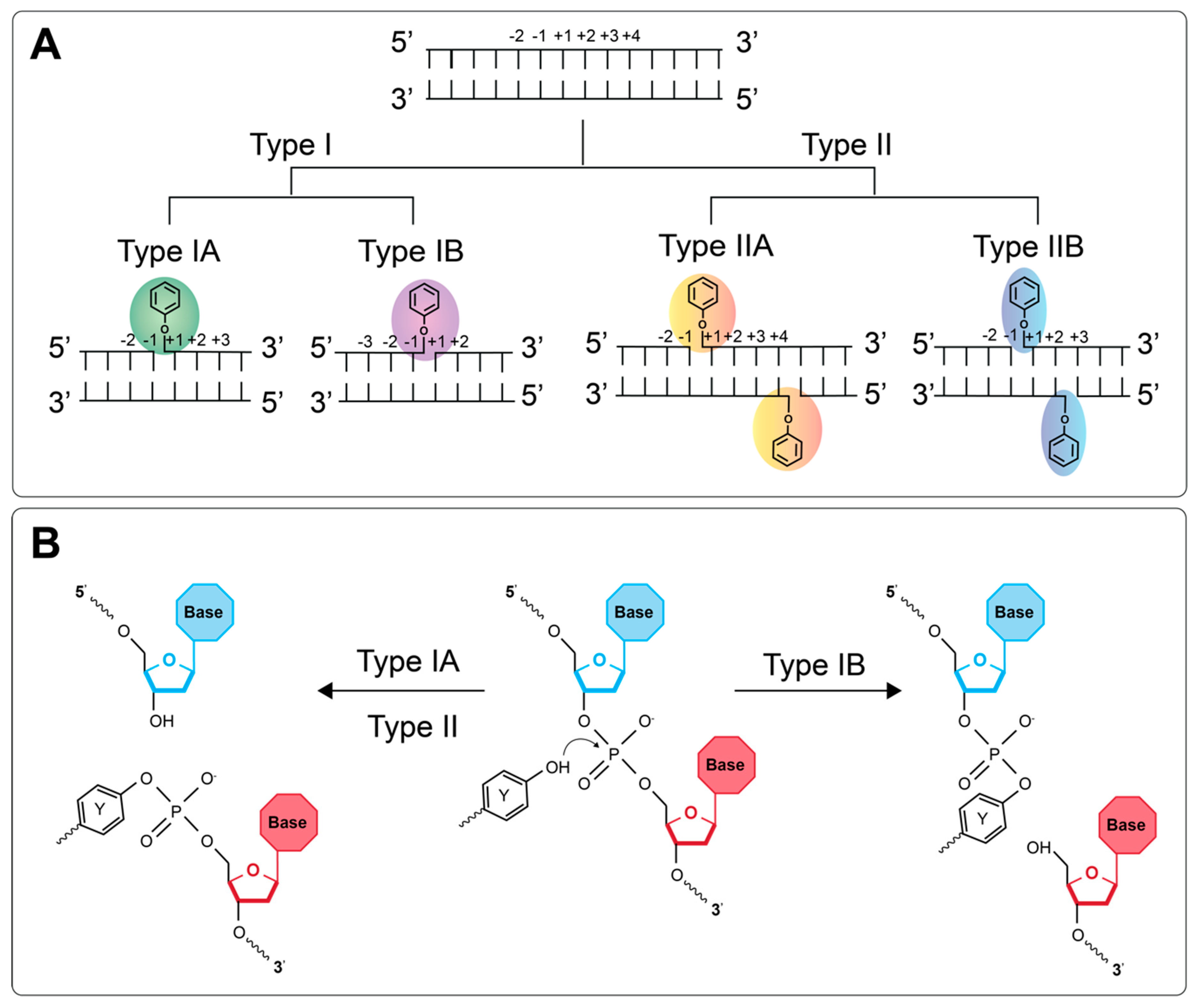
Genes Free Full Text Mapping Dna Topoisomerase Binding And Cleavage Genome Wide Using Next Generation Sequencing Techniques Html

What Are The Similarities Between Helicases And Topoisomerases How Do They Differ From Each Other Quora

The Many Lives Of Type Ia Topoisomerases Journal Of Biological Chemistry

Schematic Illustration Of Topoisomerase I Topi Left And Ii Topii Download Scientific Diagram
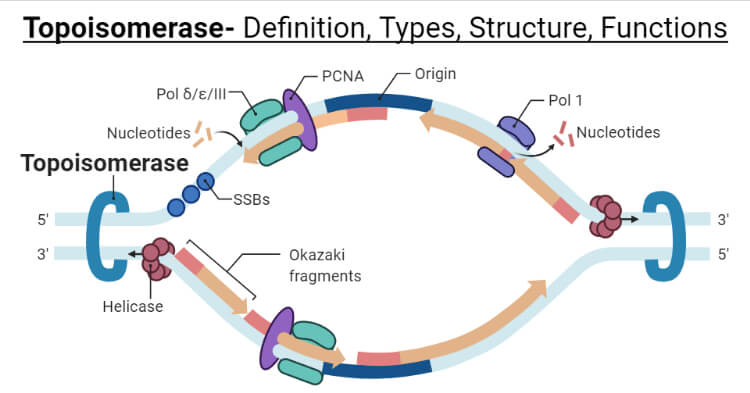
Topoisomerase Definition Types Structure Functions Mechanism

Difference Between Topoisomerase I And Ii Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms

Structure And Mechanism Of Type Ii Topoisomerases A Type Iia Topo Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment